ctys-VMW-Configuration
October, 2010
.
VMW - Basics for Operations
The ctys-VMW plugin defines a meta-layer for an abstract interface, which is
in current version based on the final commandline call of the supported products.
The ctys-VMW plugin supports a subset of the products native command line options
mapped to the ctys call options, the remaining are bypassed as native options.
Future versions are going to provide an abstract encapsulation layer by a common ctys-wrapper script
and in addition utilization of the vendor provided management interfaces for batch-mode
installation and operations.
The call structure fits into the common structure of ctys but for the current version the
ctys-wrapper script is not yet supported for the VMW subsystem.
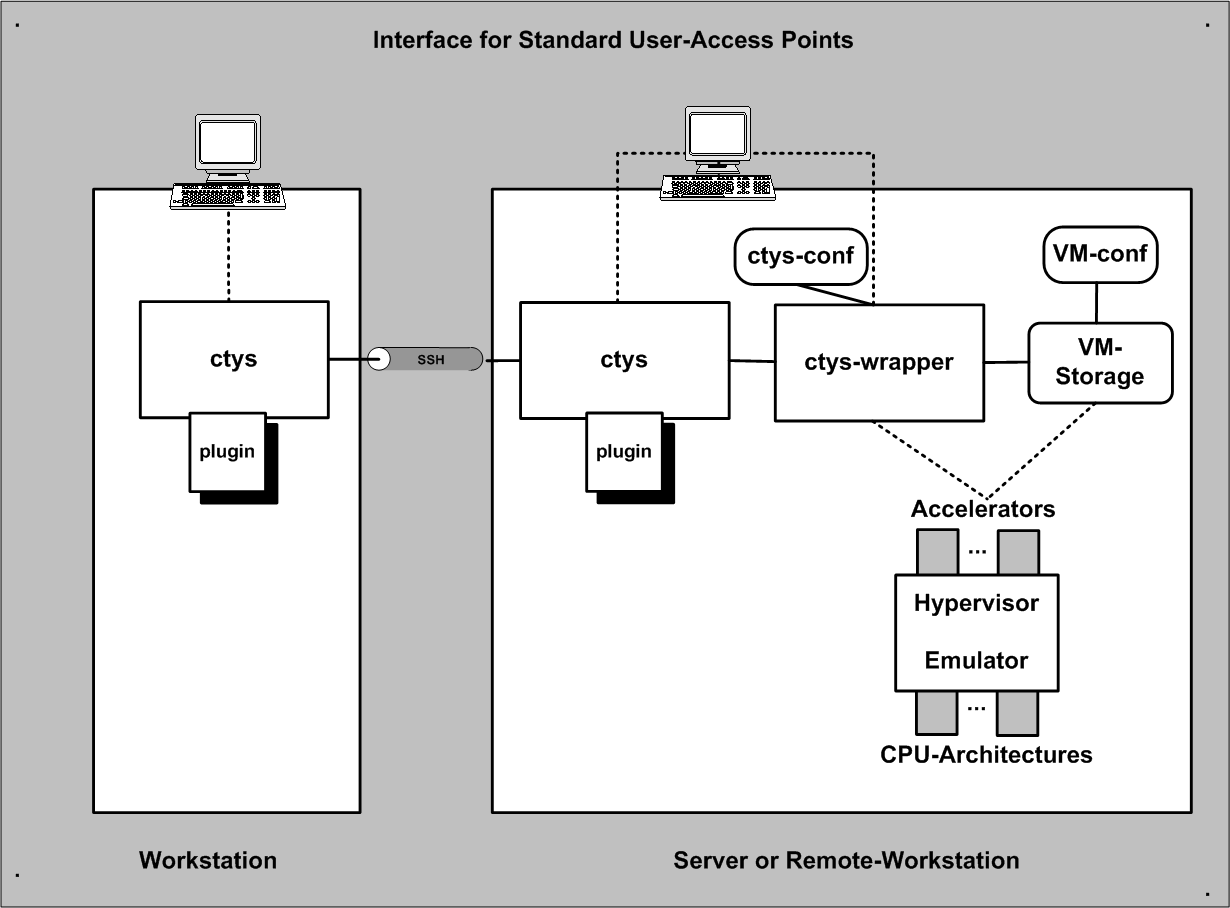
| Interfaces for Access Points |
The VMW subsystem supports the standard configuration files created by the vendor
utilities.
Thus any existing installation with any already present VMs and vmx-files could be used without
required adaptation.
These could be either used by dynamic addressing, dynamic search, or by unmodified scan into the inventory database.
The creation of new VMs is foreseen by the standandard procedures as defined by the vendor and supported
by the products.
- REMARK:
-
The current version requires the access to the VMX-configuration-files, thus these have to be either
registered in the UnifiedSessionsManager inventory database, or provided by the call sub-options for
scan-start base:, or by explicit addressing id:.
For newer versions e.g. of VMware-Server-2x(TM) in case of usage of subdirectories for the actual
storage of the virtual devices, the configuration and management information is probably still stored
in the root of the configured storage.
This should be post-merged manual with the virtual device into a unique shared directory comprisingly
representing the VM.
The lack of the standard vmx-files is the missing of offline information about the GuestOS.
The UnifiedSessionsManager provides for basically two options for the coallocated storage of
additional extended GuestOS information.
- Coallocated ctys-configuration-file created by
ctys-createConfVM(1)
- Extension of the vendor configuration file by ctys-keywords within comment-protected strings
The ctys-configuration-file is defined by convention to be stored within the directory of the virtual machine,
coallocated with the vmx-file and named with the same prefix as the vmx-file: <vmx-file-prefix>.ctys and
the containing directory ..../<vmx-file-prefix>.
Even though this probably could varied, this has to be avaoided due to probable unanounced remove of the required features.
The file could be created and added manually by the user with the same following optional "ctys-conf" vmx-file modifications
and by the previous naming convention.
Alternatively the keywords could be stored within the vmx-file, due to the key-prefixes defined to begin
with a valid vmx-comment character these are protected for unintended evaluation by the hypervisor.
The provided example may suffice the most required offline information for the user-management
of the VM, including the automated generation of a cache database for the network inventory.
#@#MAGICID-VMW
#@#VMSTATE="ACTIVE"
#@#SERNO="20080415051600"
#@#VERSION="01.01.001"
####MAC0 is provided by the eth0 of vmx-file!
#@#IP0="192.168.1.235"
#@#DIST="CentOS"
#@#DISTREL="5"
#@#OS="Linux"
#@#OSREL="2.6"
#@#CATEGORY="VM"
The current version is supported by the interactive installer
ctys-createConfVM(1)
which creates an appropriate addon-configuration file.
For examples of CentOS installation as GuestOS refer to
ctys-uc-CentOS(7).
Once VMW is setup, the boot of the VM could be performed by the CREATE action of ctys.
Basic Use-Cases for application are contained within the document
ctys-uc-VMW(7).
Supported HOST-OSs
The VMW plugin is supported on all released runtime environments of the
UnifiedSessionsManager where the products are available.
Supported GuestOSs
The native GuestOS support is the same as for the PMs and HOSTs plugins.
Supported Architectures
The whole set of available CPUs by Products is supported :
x86, AMD64, x86_64
Supported Interfaces
Current version supports the commandline interfaces of the products.
Supported VM Management Interfaces
The current version supports for basic management facilities by a
vendor provided tools.
These comprise mainly the creation of runtime entities and the cancellation
of running instances a.k.a sessions.
Library functions for vendor provided coding interfaces are due to the lack of
actual requiremtn not utilized yet.
The interface for the commandline based tools varies between the producty and versions.
The additional requirements such as a valid account with appropriate permissions including
the actual call interface may vary, e.g. for vmrun between Server-1.0.10 and Server-2.0.2.
The following tools are utilized for now as required:
- vmware
- vmplayer
- vmware-cmd
- vmrun
Network Interconnection
- NIC-bonding
-
The Installation of VMware is quite forward.
Only some minor pitfalls occur for specific configurations with
NIC-bonding.
When a bonding device is utilized on Linux the mode=6 is not supported, which is the
ARP-negotiation of client and server machines.
The success of the support could be easily checked when using a guest
system and calling ping.
The effect is the lost of about the half of the ping-answers.
This is somewhat a pity, because the mode=6 seems to be the fastest
mode which even does not require support of intermediate network equipment.
Any other mode seems to work properly.
Installation of Components
The provided examples are based - if not stated else - on CentOS-5.4, but may
be applicable for any other distribution similar.
- Server-1.0.10
-
The installation of VMware-Server(TM)-1.0.10 on CentOS-5.4
depends on the used kernel.
The description is verified to be applicable to linux-2.6.29.
- Download and install rpm of product from VMware(TM) Inc. e.g. VMware-server-1.0.10-203137.i386.rpm
- Install new kernel, here linux-2.6.29.
- Install init_mm patch for kernel and configure build-parameters.
Set kernel-parameter for "Kernel-Hacking" activate "EXPORT UNUSED
SYMBOLS"
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
- Build kernel.
- Install patches for "/usr/lib/vmware/modules/sources".
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
- Reboot.
- Configure vmware: vmware-config.pl
- Server-2.0.2
-
The installation of VMware-Server(TM)-2.0.2 on CentOS-5.4
depends on the used kernel.
- Common
- Download and install rpm of product from VMware(TM) Inc. e.g.
VMware-server-2.0.2-203138.x86_64.rpm
- For CentOS-5.4 - install glibc-patch and edit "/usr/sbin/vmware-hostd" script.
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
- Athentication with Kerberos
For the following distributions the procedures are verified.
But as far as known only the credentials/password are fetched
form Kerberos.
Currently - eventually due to knowledge-lack - missing the
full SSO.
The only file required be modified is '/etc/pam.d/vmware-authd'.
- Reboot.
- After creation of the first additional user within the VMware GUI, the counter/index
for the next user has to be once incremented manually within the file
'/etc/vmware/hostd/authorization.xml'.
Else the creation of additional users fail with the error message expressing unavailability
of the database.
- Standard kernel-2.6.18
- Configure vmware: vmware-config.pl
- New kernel-2.6.32.6
-Install, configure, and build the new kernel, here linux-2.6.32.6.
- Install patches for "/usr/lib/vmware/modules/sources".
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
- Configure vmware: vmware-config.pl
- Standalone Console
- Extract plugin for standalone console from Server installation
and install this at "/opt/vmware/vmware-wmrc-x64".
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
- Install "xdg-utils".
- Player-1.0.5
-
Install the rpm package VMware-player-1.0.5-56455.i386.rpm for the standard kernel linux-2.6.18-164.el5.
- Player-2.5.3
-
Install the rpm package VMware-player-1.0.5-56455.i386.rpm
for the standard kernel linux-2.6.18-164.el5.
- Player-3.0.1
-
Install the bundle-package VMware-Player-3.0.1-227600.x86_64.bundle
for the standard kernel linux-2.6.18-164.el5.
- Workstation-6.5.3
-
Install the bundle-package VMware-Workstation-6.5.3-185404.x86_64.bundle
for the standard kernel linux-2.6.18-164.el5 and execute vmware-config.pl.
- Workstation-7.0.1
-
Install the bundle-package VMware-Workstation-Full-7.0.1-227600.x86_64.bundle* for the standard kernel linux-2.6.18-164.el5.
- Standalone Console VMWRC
-
-
Extract plugin for standalone console from Server installation
and install this at
"/opt/vmware/vmware-wmrc-x64".
The patch could be downloaded from www.i4p.com.
-
Install "xdg-utils".
Install Procedures
- General Remarks
-
The most of the installation is performed with PXE if possible.
Therefore the PXELINUX is switched to version 3.6.2 and a menu system
for the management of the whole test-environment is setup.
When difficulties occur due to specific network requirement, the
CD-mount on ISO files option is used, which is almost in any case
experienced to be quite safe for VMware products.
- Installation and Maintenance by Product Console
-
For initial creation or basic maintenance the console of the specific product has to be started.
The following options are available.
| Product |
Version |
Available Console |
| Server |
1.x |
Proprietary |
| Server |
2.x |
Browser, VMWRC |
| Workstation |
x |
Proprietary, VNC |
| Player |
- |
- |
| Overview of product specific consoles |
The console could be started e.g. by usage of the X11 plugin.
This is the case for the 2.x versions of the Server-Products.
ctys -t x11 \
-a create=l:vmware,cmd:firefox%http:://127.0.0.1::8222 \
delphi
The double column masks this character as a native to be bypassed, else
it would be interpreted as a seperator of subarguments.
The non-SSL port is required in some cases, where the other is not operable.
Any X11 program could be executed, e.g. the proprietary console by:
ctys -t x11 \
-a create=l:vmware,cmd:vmware \
delphi
- Create a VM for Server-2.x
The example installation here is based on Server-2.0.2 and debian-5.0.0/amd64
installed by ISO image from a mounted local storage.
- Start remote console by browser. Here as non-encrypted.
ctys -t x11 \
-a create=l:vmware,cmd:firefox%http:://127.0.0.1::8222 \
delphi
Here the non-encrypted local port is utilized, whereas the encrypted port
is the default.
It is recommended to use a the "Product Compatibility" for
"Virtual Hardware" as "4" or "6".
This assures the presence of a vmx-file.
- Create a VM by 'Create Virtual Machine' command entry and perform the
required steps. The following steps assume an ISO image as the install media.
- Start the VM by calling:
ctys -t vmw \
-a create=l:debian-5.0.0,console:vmwrc,user:acue,\
p:/mntn/vmpool/vmpool01/vmw/templates/debian-5.0.0 \
delphi
This enters the native install procedure of the debian distribution.
- Start installation by choosen install media.
- PXE-Boot
-
The folowing steps are applied to an installation by PXE.
This anyhow requires the proper setup of DHCP, TFTP, and one of
HTTP/FTP/NFS.
For some OSs a so calld kickstart file could be used to automate the
whole procedure.
For Linux and BSD refer to
SYSLINUX
and
ETHERBOOT.
- Create a VM by native means of a VMware product, but do not start it yet.
When the base machine is created, close the VM.
The common convention within ctys is, that the following items are all
literally the same.
- LABEL
- DisplayName
- <vmx-filenameprefix>
- <directory-containing-vmx>
- Edit the VMX file manually and apply following changes and addons:
- Check "displayName" as mentioned before.
- Change the ethernet interface entries for the MAC-address
and behaviour as required for PXE/DHCP.
- The default behaviour is described as "generatedAddress", which could
change and is somewhat challenging to be continuously maintained for PXE/DHCP.
Therefore it should be changed to "static".
The resulting entries depend on the actual product, but the essential
entries seem to be common as for following example:
- ethernet0.present = "TRUE"
- ethernet0.addressType = "static"
- ethernet0.address = "00:50:56:13:11:4D"
- When the cache database is already populated by values from
/etc/dhcpd.conf or a manually created database similar to
/etc/ethers, the utility
ctys-macmap
could be used for management of address-mappings.
- Change the UUID entries from dynamic behaviour to static values,
otherwise they will change when the machine is reallocated.
The values could be kept as already present, else should be generated
by "uuidgen".
- uuid.action = "keep"
- uuid.location = "56 4d 66 ff 5a 76 d1 19-35 11 73 3d 0f 8d 26 9a"
- uuid.bios = "56 4d 5e 88 71 0e a5 79-59 6c 34 15 44 a7 7e 96"
- Add ctys-meta information as required for ENUMERATE.
Additional values might be applied to the following example.
The values are not recognized by VMware, thus has to be kept
synchronous by the user.
The main intention is to get cacheable information for off-line guests
to be utilized by
and therefore by
ENUMERATE and therefore by ctys-vhost
#@#MAGICID-VMW
#@#VMSTATE="ACTIVE"
#@#SERNO="20080415051600"
#@#VERSION="01.01.001"
####MAC0 is provided by the eth0 of vmx-file!
#@#IP0="192.168.1.235"
#@#DIST="CentOS"
#@#DISTREL="5"
#@#OS="Linux"
#@#OSREL="2.6"
#@#CATEGORY="VM"
- Close the file within the editor and open it again within the VMware frontend.
- From now on the following steps could be already proceeded either by native
call of "vmware", or by usage of the UnifiedSessionsManager, which has
some advances for monitoring and
LIST
of current active sessions.
The following example illustrates the call, when for a new machine the
<machine-adress>
is not yet registered within the
cacheDB(ctys-vdbgen)
ctys -t vmw \
-a create=p:$HOME/vmware/tst-ctys/tst116/tst116.vmx,reuse \
-c off \
-C off \
host1
- Start the VM and set the emulated BIOS appropriately, by entering with *F12*.
- Boot into PXE, which might be a simple or more advanced Menu, or just
a command line for entering a boot string
SYSLINUX.
- Install by means of current GuestOS and/or any generic installer.
- ISO-Image and DHCP
-
The install procedure for usage of an ISO-Image is almos the same as
for PXE, just a few formal differences apply.
- Add a CD/DVD-ROM-drive with a link to an ISO-Image, similar to
an actual physical drive.
- Select the appropriate boot order, where instead or in addition to PXE
the CD/DVD-drive has to be registered.
- Remote Console for 2.x-versions - vmware-vmrc
-
The remote console plugin of the Server-2.0 versions could be started standalone
too, thus integrates seamless as a graphic terminal into ctys.
The compressed plugin for various architectures is stored in the directory:
/usr/lib/vmware/webAccess/tomcat/apache-tomcat-6.0.16/webapps/ui/plugin
This directory contains the files:
- build_doNotErase.txt
- vmware-vmrc-linux-x64.xpi
- vmware-vmrc-linux-x86.xpi
- vmware-vmrc-win32-x86.exe
- vmware-vmrc-win32-x86.xpi
-
These can be uncompressed with unzip, the plugins directory is the
only subdirectory required, which contains the executable vmware-vmrc.
This requires the containing directory as base for relative search for shared libaries,
thus should be the call directory for simplicity.
In ctys it is in current pre-configuration expected this directory to be renamed and
located as one of the following directories. These are searched in the given order until first
match.
- ${MYADDONSPATH}/vmware-rc-x64
The advance is here, that the whole package is distributed together with ctys when using
ctys-distribute with a file copy mode.
- ${HOME}/vmware/vmware-rc-x64
- /opt/vmware/vmware-rc-x64
- /usr/bin
- /usr/local/bin
- /usr/share/vmware-rc
- /usr/share/vmware-rc-x64
- /usr/share/vmware-rc-x86
- /opt/bin
- /opt/vmware/vmware-rc
When calling ctys with the console type VMWRC now it should be considered whether the password
will be provided by commandline or inserted into the dialogue mask when omitting.
An alternative is the Single-Sign-On configuration.
The resulting call could be :
ctys -t vmw \
-a create=l:tst502,reuse,user:root%tst,console:vmwrc \
-c local root@lab02
- Supported/Tested Install-Mechanisms
-
The current version relies on the provided intstall mechanisms of the product
supplier, and pre-requires an installed system.
Installation of GuestOS
- CentOS-5
-
Installation is in general quite straight-forward.
Here performed by PXE on a i386 machine with one CPU.
- Debian-4.0_r3
-
Installation is quite straight-forward, once the required additional
netboot-image is downloaded and in place.
The differences and additions to the predefined environment are:
-
Only the kernel image "linux" and the ramdisk "initrd.gz" are imported into a common boot
environment with several UNIX variants as provided by
SYSLINUX.
-
The following key has probably to be applied
debian-installer/allow_unauthenticated=true
- Debian-5.0.0
-
Refer to the example in chapter "Installation and Maintenance by Product Console".
- Fedora 8
-
Installation is quite straight-forward and very similar to CentOS.
- MS-Windows-NT-4.0-S
-
Installed from ISO image.
- MS-Windows-2000-WS
-
Installed from ISO image.
- OpenBSD
-
Installation is quite straight-forward, just the two-level boot has to
be considered.
- SuSE
-
Installation is quite straight-forward.
Installed Systems
| OS |
name |
Inst-VM |
Media |
| CentOS-5.0 |
tst117 |
Server-1.x, 2.x |
PXE,ISO |
| CentOS-5.1 |
tst112 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE,ISO |
| CentOS-5.2 |
tstxxx |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE,ISO |
| CentOS-5.3 |
tstxxx |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE,ISO |
| CentOS-5.4 |
tst131 |
Server-1.0.10, 2.0.2 |
PXE,ISO |
| CentOS-5.5 |
x |
Server-2.0.2 |
PXE,ISO |
| Debian-4.0r3 |
tst106 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE,ISO |
| Debian-5.0.0 |
tst200 |
Server-1.0.10 |
PXE,ISO |
| Debian-5.0.0-amd64 |
debian-5.0.0 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Fedora 8 |
tst103 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| Fedora 10 |
tstxxx |
Server-1.0.10 |
ISO |
| Fedora 12 |
tst201 |
Server-1.0.10 |
ISO |
| FreeBSD-7.1 |
tst208 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| FreeBSD-8.0 |
tst209 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Gentoo-2009 |
(tst231) |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Mandriva-2010-free |
tst227 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Mandriva-2010 |
tst203 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| OpenBSD-[2-4] |
tstXYZ |
WS5/6,Server-1.0.[1-5] |
PXE,ISO |
| OpenBSD-4.0 |
tst109 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| OpenBSD-4.2 |
tstxxx |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| OpenBSD-4.3 |
tst155 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| OpenBSD-4.6 |
tst207 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| ScientifiLinux-5.4.1 |
tst204 |
Server-1.0.10 |
PXE,ISO |
| SuSE-9.3 |
tst003 |
WS6,Server-1.0.[345] |
PXE,ISO |
| OpenSuSE-10.3 |
tst116 |
WS6,Server-1.0.[345] |
PXE,ISO |
| OpenSuSE-11.2 |
tst205 |
WS6,Server-1.0.[345] |
PXE,ISO |
| Solaris 10 |
tst115 |
WS6 |
ISO |
| OpenSolaris 2009.6 |
tst242 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Ubuntu-6.06.1-D |
tst128 |
Server-1.0.4 |
ISO |
| Ubuntu-6.06.1-S |
tst120 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| Ubuntu-7.10-S |
tst005 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| Ubuntu-8.04-D |
tst132 |
Server-1.0.4 |
ISO |
| Ubuntu-8.04-S |
tst133 |
Server-1.0.4 |
PXE |
| Ubuntu-9.10-D |
tst133 |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| Ubuntu-10.10-D |
tstXYZ |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| MS-Windows-2000WS |
tstXYZ |
WS4/5/6,Server-1.0.[1-5] |
PXE,ISO |
| MS-Windows-2000S |
tstXYZ |
WS4/5/6,Server-1.0.[1-5] |
PXE,ISO |
| MS-Windows-2003S |
x |
Server-2.0.2 |
ISO |
| MS-Windows-XP |
tstXYZ |
WS4/5/6,Server-1.0.10 |
PXE,ISO |
| MS-Windows-NT-4.0S |
tstXYZ |
WS4/5/6,Server-1.0.[1-5] |
PXE,ISO |
| Overview of Installed-VMs |
SEE ALSO
ctys(1)
,
ctys-createConfVM(1)
,
ctys-VMW(1)
,
ctys-uc-VMW(7)
,
ctys-plugins(1)
,
ctys-vhost(1)
,
vmware(1)
ctys-uc-CentOS(7)
PXE-SYSLINUX-PXELINUX-ISOLINUX: <http://syslinux.zytor.com>,
PXE-ROM-Images-Etherboot: <http://www.etherboot.org>
AUTHOR
Written and maintained by Arno-Can Uestuensoez:

COPYRIGHT
Copyright (C) 2008, 2009, 2010 Ingenieurbuero Arno-Can Uestuensoez
For BASE package following licenses apply,
- for software see GPL3 for license conditions,
- for documents see GFDL-1.3 with invariant sections for license conditions,
This document is part of the DOC package,
- for documents and contents from DOC package see
'Creative-Common-Licence-3.0 - Attrib: Non-Commercial, Non-Deriv'

with optional extensions for license conditions.
For additional information refer to enclosed Releasenotes and License files.


