.
ctys-uc-debian-5 - Use-Cases for Setup of debian
The current document shows the basic installation of Debian.
The following host environment is used here:
The following client environment is used here:
The following common assumptions and simplifications are choosen, when multiple approaches are valid.
.
The installation for the following variants has to be performed by the appropriate standard setup of the HostOS, which quite straight forward:
ctys-distribute -F 2 -P UserHomeCopy root@myHostFor short
ctys-distribute -F 2 -P uhc root@myHost
ctys -t cli -a create=l:myHost root@myHost
ctys-plugins -T all -E
The following steps are required for a RPM based setup on CentOS. The installation is relocatable, but located at '/opt', and installed locally by 'ctys-distribute'.
rpm -i ctys-base-01.11.011.noarch.rpm
/opt/ctys-01.11.011/bin/ctys-distribute -F 2 -P UserHomeCopy
ctys-xdg --menu-create
The setup of the Gnome Menu is quite simple, the contained tool ctys-xdg sets up a standard menu by the call:
ctys-xdg --menu-create

The call
ctys-xdg --menu-cancel
removes the installed files. For current version no checks for changed files is done.
The menues could be edited and extended by the call
ctys-xdg --menu-edit
which opens the related directories for modification of '*.menu', '*.desktop', and '*.directory' files.
The demo example VM is here named tst004, this is the hostname of GuestOS too.
ssh -X app2When just the processing node of mounted filesystem has to be changed, the following call could be applied. This works in case of identical mount paths:
ctys -t cli -a create=l:tst004,cd:$PWD root@lab02
mkdir tst004
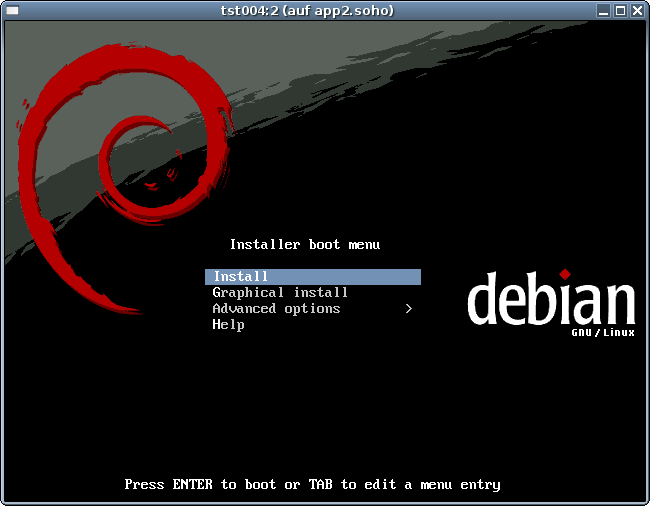
ARCH=x86_64 \ DIST=debian \ DISTREL=5.0.6 \ OS=Linux \ OSREL=2.6.32-6 \ ctys-createConfVM -t qemu --label=tst004This call creates a virtual image(hda.img), the call-wrapper(tst219.sh), and the configuration file(tst004.ctys). The files are created from templates by assigning configuration values either from pre-configured default values, or interactive variation. The whole process of createion could be batch-proceeded by using the either teh --auto, or the --auto-all option when appropriate default values are preconfigured. When no MAC database nor DHCP is available, the MAC and IP addresses might be provided too.
./tst004.sh --console=vnc --vncaccessdisplay=47 --print --instmode --check
./tst004.sh --console=vnc --vncaccessdisplay=47 --print --instmodeAlternatively a remote call could be proceeded:
ctys -t qemu -a create=l:tst004,b:${VMPATH},instmode app2
ctys -t qemu \
-a create=l:tst004,id:${PWD}/tst004.ctys,console:vnc \
app2
The default console is here VNC.
The creation of the raw VM is the first step to be executed at the host operating system. This could be either performed locally or remote and requires the usage of the provided tools by VirtualBox(TM).
ssh -X lab02
VirtualBox
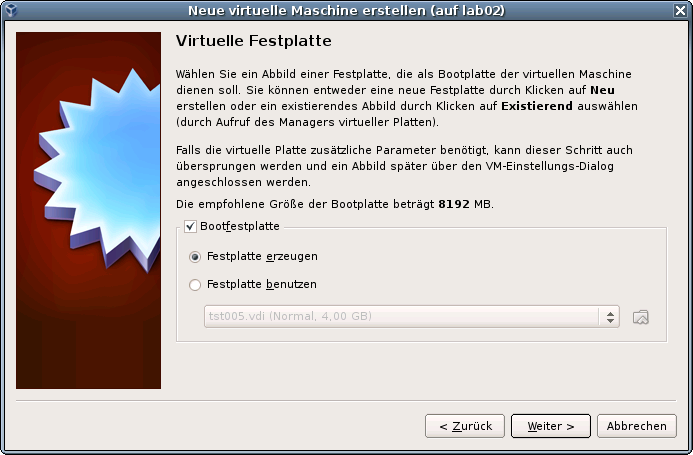
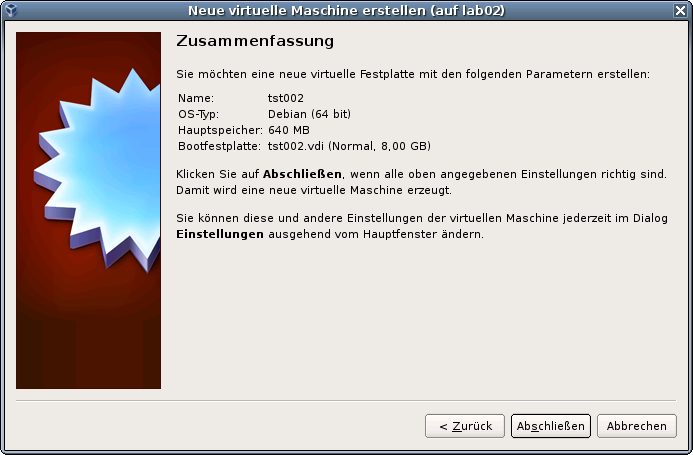
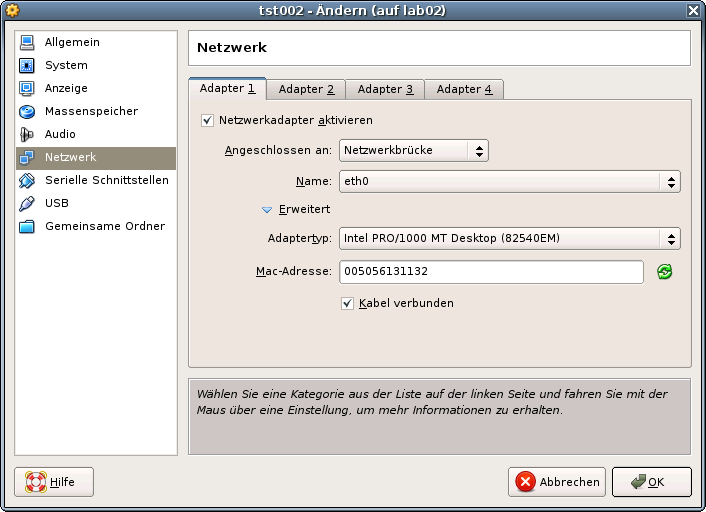
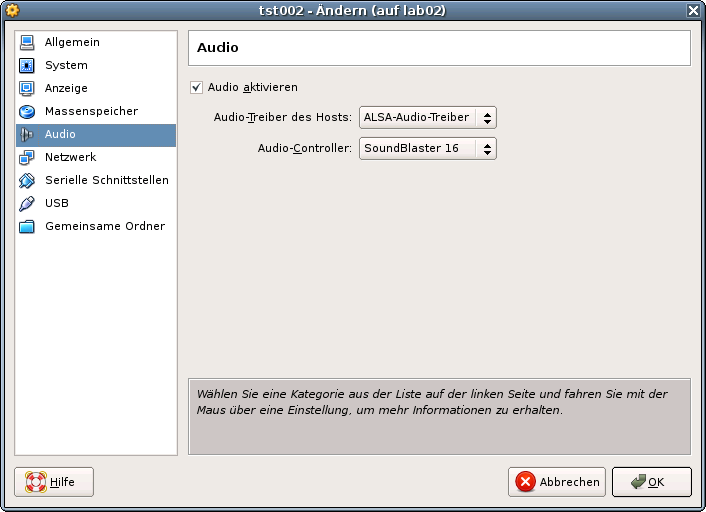
DIST=debian \ DISTREL=5..6 \ OS=Linux \ OSREL=2.6-26.2 \ ctys-createConfVM -t vbox --label=tst002 --levo
Not all values require to be set, some will be requested later by
dialogue.
Thus it is not neccessary to have values assigned to the complete
displayed set.
Actually used sources for default values:
no-marker = Pre-Set value, either from defaults configuration,
or by commandline.
no-value = Either requested by dialog later, or the defaults
of the finally called application are used.
(c) = Read from actual configuration file, e.g. vmx-file.
(d) = Read from database.
(g) = Dynamically generated.
(h) = Used from current host as default.
(m) = Received from mapping definitions.
Applicable modifications:
blue = By call option, defines dependency for others.
green = By environment, 'could be set almost independent'
from other values.
cyan = By miscellaneous facilities, but is dependent from
others.
E.g. LABEL defines by convention the network 'hostname',
thus the TCP/IP params.
This could ..., but should not be altered!
Most of the missing values will be fetched during actual execution of
this tool by dynamic evaluation.
VAR name:Initial Value
C_SESSIONTYPE:VBOX
LABEL:tst002
MAC:00:50:56:13:11:32 (c)
IP::172.20.2.132 (m)
BRIDGE:
DHCP:
NETMASK:
TCP:tst002 (m)
GATEWAY:
EDITOR:root
UUID:a610968d-8cfd-40d1-bf26-30c72e0f4684 (c)
DIST:debian (h)
DISTREL:5.0.6 (h)
OS:Linux (h)
OSREL:2.6.26-2-amd64 (h)
ARCH:x86_64 (h)
ACCELERATOR:VT (c)
SMP:1 (c)
MEMSIZE:640 (c)
KBD_LAYOUT:de
STARTERCALL:/usr/bin/VirtualBox
DEFAULTBOOTMODE:HDD
DEFAULTINSTTARGET:/mntn/vmpool/vmpool05/vbox/test/...
...tst-ctys/tst002/tst002.vdi
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_SIZE:8192M
DEFAULTHOSTS:VNC
DEFAULTCONSOLE:RDP
VMSTATE:ACTIVE
Remember that his is a draft pre-display of current defaults.
No consistency-checks for provided values are performed at this stage.
Some missing values are evaluated at a later stage dynamically.
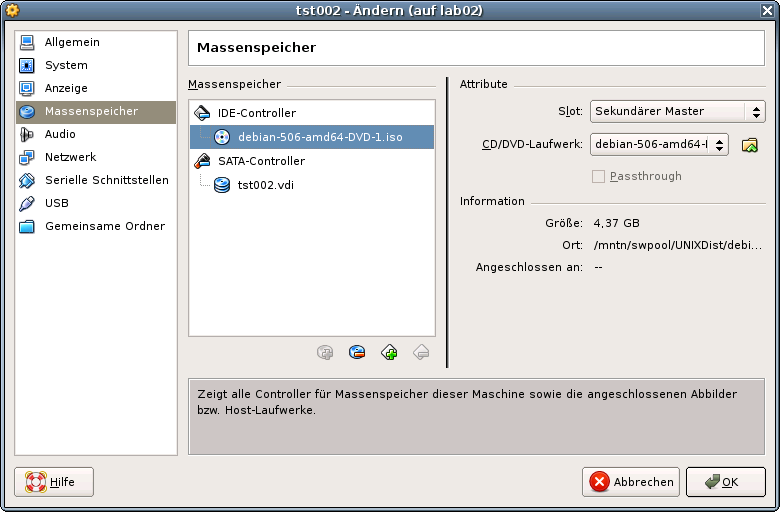
VirtualBoxThe following call variant starts the remote VM with a VirtualBox console:
ctys -t vbox \
-a create=l:tst002,id:${TST002}/tst002.ctys,console:vbox\
lab02
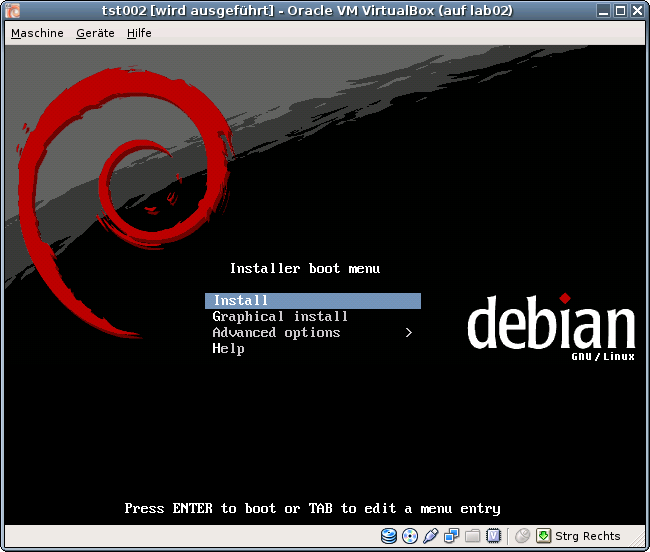
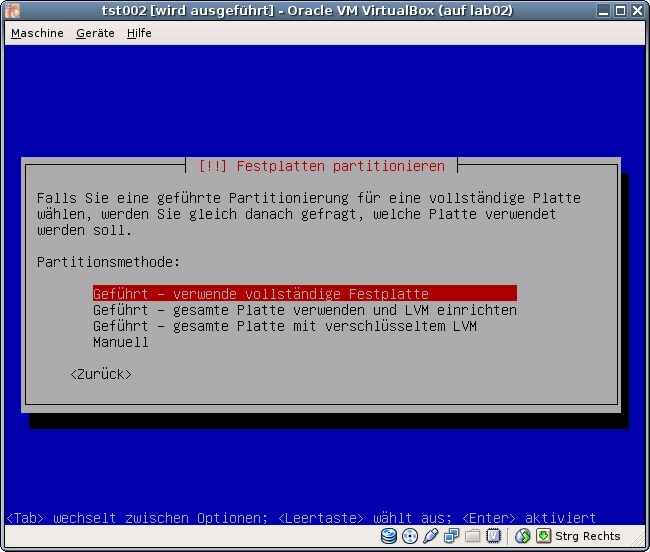
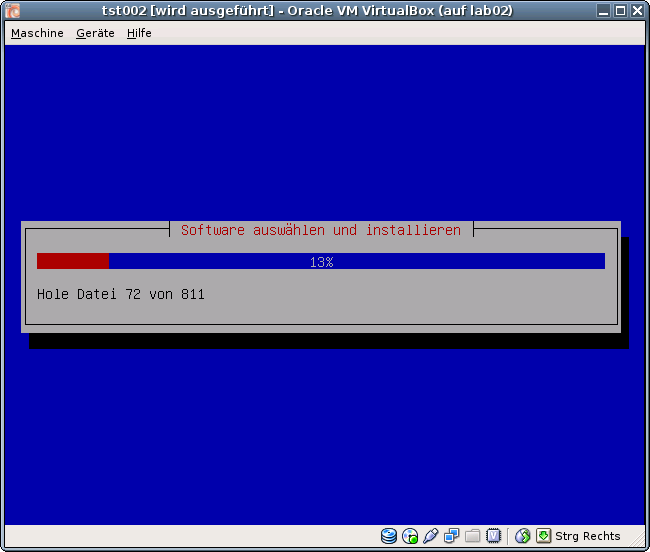
ctys -t vbox \
-a create=l:tst002,id:${PWD}/tst002.ctys,console:vbox \
lab02
The default console is here RDP.
In case of a common mounted NFS filesystem for the pool VMs for simplicity just change into the directory of the VM on any machine. Call for the first check ctys-vdbgen with the --stdio option for display only.
ctys-vdbgen --append --base=$PWD --stdio -- lab02
When the result is displyed correctly just call
ctys-vdbgen --append --base=$PWD -- lab02
The following output should be displayed:
Prepare execution-call:
Require DB-PATH, USE: DEFAULT_DBPATHLST="/homen/acue/.ctys/db/default"
Require DB-PATH, USE: -o => "/homen/acue/.ctys/db/default"
APPEND mode : ON(1)
STDIO mode off : OFF(0)
Set TYPE scope ADD: DEFAULT="-t ALL"
Preload TYPE set ADD: DEFAULT="-T ALL"
For splitted operations ADD: DEFAULT="-b sync,seq "
Nameservice cache OFF: DEFAULT="-c off "
Data cache OFF: DEFAULT="-C off "
Resulting ENUMERATE ADD: DEFAULT="-a enumerate=...
...matchvstat:active%disabled%empty,machine,\
b:/mntn/vmpool/vmpool05/vbox/test/tst-ctys/tst137 \
-C off -c off -T ALL "
-> generate DB(may take a while)...
-----------------------------------
START:08:38:35
------
------
END:08:39:03
DURATION:00:00:28
-----------------------------------
RET=0
-----------------------------------
Cached data:
Mode: APPEND
Pre-Appended: 834 records
Appended: 1 records
Fetched Records Raw: records
Fetched Records Unique: records
Final: 835 records
-----------------------------------
...finished.
This shows that only one entry is appended to the existing database with 834 VM-Entries. Now check the database entry by calling:
ctys-vhost tst137
The following result should be displayed:
label |stype|accel|distro|distrorel|os |osrel|PM |if |TCP ------+-----+-----+------+---------+-----+-----+-----+---+------------ tst137|VBOX | |CentOS|1.0.0 |Linux|2.6 |lab02|0 |172.20.2.241
Now call the menue item for start of the VM 'tst137'.
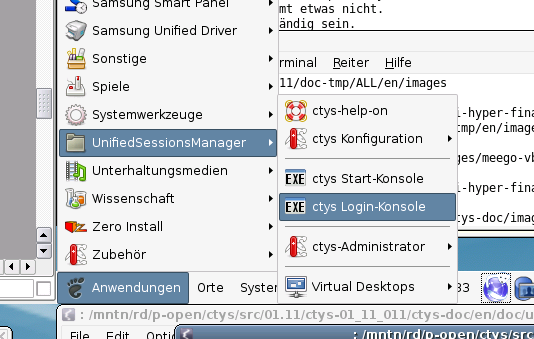
The created cacheDB record for thr VM 'tst137' is now automatically visible in the
list of startable virtual machines.
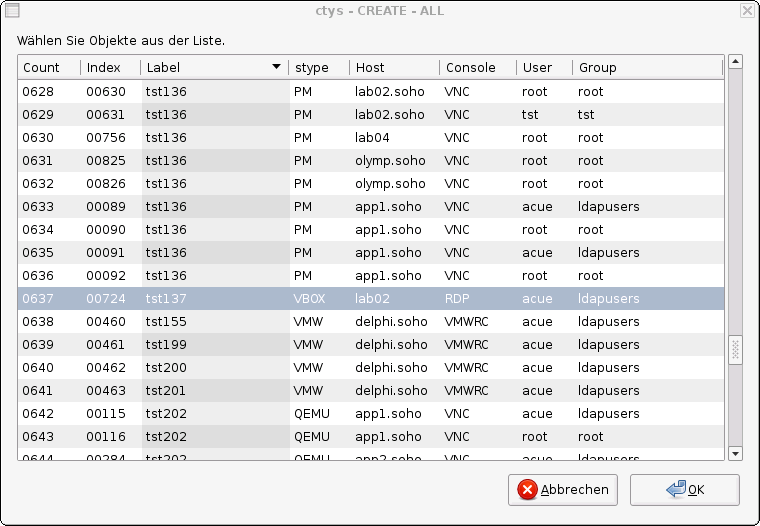
Confirm the selected entry.
Almost absolutely required is a Single-Sign-On facility for OpenSSH. This is due to the required multiple remote remote calls for a number of operational modes. Recommended is either the usage of SSH-Keys, or Kerberos by GSSAPI.
Apply standard procedure:
ctys-distribute -F 2 -P UserHomeCopy root@tst137
Call CLI plugin:
ctys -t cli -a create=l:tst137 root@tst137
Call ctys-plugins:
ctys-plugins -T all -E
ffs.
Call VNC plugin:
ctys -t vnc -a create=l:tst137,reuse root@tst137
Call VNC plugin:
ctys -t x11 -a create=l:tst137,reuse root@tst137
ctys-VBOX(1), ctys-QEMU(1), ctys-uc-VBOX(7), ctys-uc-QEMU(7), ctys-configuration-VBOX(7), ctys-configuration-QEMU(7)
| Arno-Can Uestuensoez | <https://arnocan.wordpress.com/> |
| <https://unifiedsessionsmanager.sourceforge.io/> | |
| <https://github.com/unifiedsessionsmanager> | |
 |
Copyright (C) 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2020 Ingenieurbuero Arno-Can Uestuensoez
For BASE package following licenses apply,
This document is part of the DOC package,

For additional information refer to enclosed Releasenotes and License files.