.
ctys-uc-WXP - Use-Cases for Setup of MS-Windows-XP(TM)
The current document shows the basic installation of MS-Windows-XP(TM) as a guest system. The current version allows the usage as aguest system by means of the controlling hypervisor with the seamless integrated application of basic features controlled by remote tools.
REMARK: The native support for the execution of the UnifiedSessionsManager within MS-Windows-XP(TM) is not yet available.
The following host environments are used here:
The following client environment is used here:
Some common assumptions are choosen for simplification when multiple options are available.
.
The installation for the following variants has to be performed by the appropriate standard setup of the HostOS, which is straight forward:
ctys-distribute -F 2 -P UserHomeCopy root@myHost
ctys -t cli -a create=l:myHost root@myHost
ctys-plugins -T all -E
ctys-vnetctl createfor current user or
ctys-vnetctl -u userX createfor the userX. This call requires root permissions due to the required modification of system resources related to networking interfaces.
The following steps are required for a RPM based setup on CentOS. The installation is relocatable, but located at '/opt', and installed locally by 'ctys-distribute'.
rpm -i ctys-base-01.11.011.noarch.rpm
/opt/ctys-01.11.011/bin/ctys-distribute -F 2 -P UserHomeCopy
The following steps are the same as for the tgz based install.
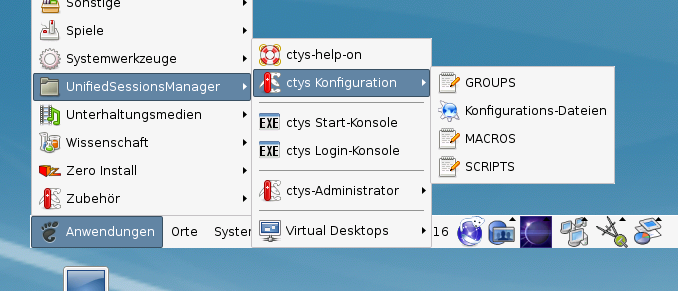
The setup of the Gnome Menu is quite simple, the contained tool ctys-xdg sets up a standard menu by the call:
ctys-xdg --menu-create

The call
ctys-xdg --menu-cancel
removes the installed files. For current version no checks for changed files is done.
The menues could be edited and extended by the call
ctys-xdg --menu-edit
which opens the related directories for modification of '*.menu', '*.desktop', and '*.directory' files.
Additional information is available by ctys-configuration-Gnome(7)
The demo example VM is here named dbms04, this is the hostname of GuestOS too.
ssh -X app2When just the processing node of mounted filesystem has to be changed, the following call could be applied. This works in case of identical mount paths:
ctys -t cli -a create=l:dbms04,cd:$PWD root@app1
mkdir dbms04
ARCH=x86_64 \
DIST=MSProducts \
DISTREL=WXP \
OS=Windows \
OSREL=XP \
MEMSIZE=784 \
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_SIZE=16G \
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_BLOCKCOUNT=64 \
HDB_ON=1 \
VIRTIONET=1 \
VIRTIOHDB=0 \
ctys-createConfVM \
-C \
-D $PWD/dbms04 \
--label=dbms04 \
--virtio \
-t qemu
This call creates a virtual image(hda.img), the call-wrapper(dbms04.sh),
and the configuration file(dbms04.ctys).
The files are created from templates by assigning configuration values either from
pre-configured default values, or interactive variation.
The whole process of createion could be batch-proceeded by using the either the --auto,
or the --auto-all option when appropriate default values are preconfigured.
When no MAC database nor DHCP is available, the MAC and IP addresses might be provided too.
The parameters VIRTIONET and VIRTIOHDB activate the use of virtio drivers for the start
of the VM.
In this case the network drivers are preconfigured to be used as paravirtualized virtio drivers,
whereas the storage uses the standard ide drivers.
Additional installation of drivers within the guest OS is required.
For information and download of virtio drivers refer to
www.linux-kvm.org
The parameter HDB_ON activates the second drive.
The image is has to be created manually, e.g. by
qemu-img create -f qcow2 drvb.img 16GThese settings could be deactivated by setting the attributes within the 'dbms04.ctys', but eventually may require additional configuration within the guest OS. For the versions MS-Windows-XP and MS-Windows-2003 the configuration has to be edited and the prepared variable ARGSADD has to be set to
ARGSADD=' -no-acpi 'in dbms04.ctys.
./dbms04.sh --console=vnc --vncaccessdisplay=47 --print --instmode --checkThe actual call assembly could be altered call-by-call e.g. by:
VIRTIONET=0 \ VIRTIOHDD=0 \ ./dbms04.sh --console=vnc --vncaccessdisplay=47 --instmode \ --print \ --checkThis deactivates the paravirtualized virtio drivers. Thus the intstallation is performed by configured standard drivers, e.g. with 'rtl8139' and 'ide' in case of MS-Windows(TM) guest OSs. The drivers could be changed later, when the appropriate drivers are installed within the guest OS by usage of standard drivers.
VIRTIONET=0 \ VIRTIOHDD=0 \ HDB_ON=0 \ ./dbms04.sh --console=vnc --vncaccessdisplay=47 --instmode \ --print \The HDB_ON parameter deactivates the drive HDB. Thus the intstallation is performed by configured standard drivers by use of the system drive only. The manual call requires to attach the console by the call similar to:
vncviewer :47&Alternatively a remote call could be proceeded, this handles the console including the assignment of a VNC access port transparently.
ctys -t qemu -a create=l:dbms04,b:${VMPATH},instmode app2
In this case the application of additional parameters by command line assignment of shell variables
is not supported, thus the configuration file is used as present.
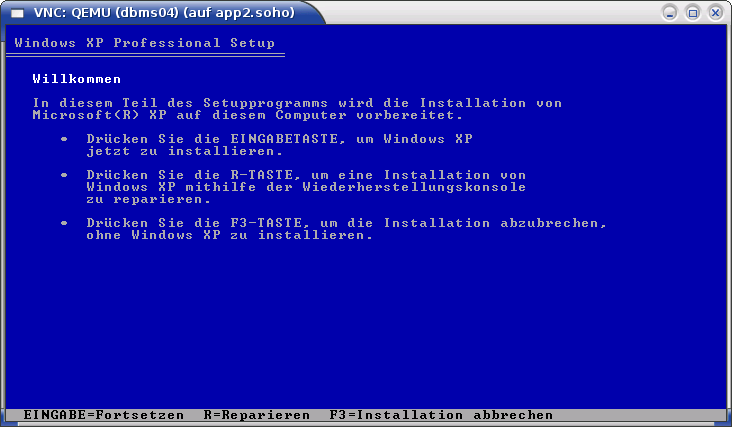
For additional information on QEMU/KVM refer to ctys-configuration-QEMU(7) .
The creation of the raw VM is first step to be executed at the host oeprating system. This could be either performed locally or remote and requires the usage of the provided tools by VirtualBox(TM).
ssh -X lab02
VirtualBox &
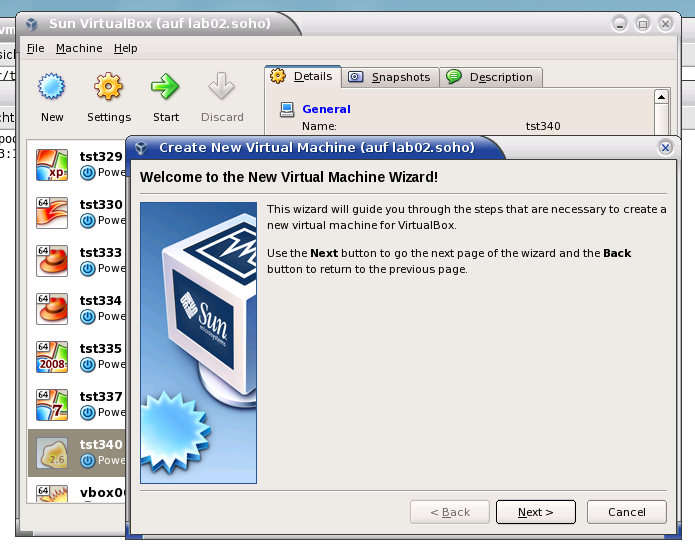
ctys-createConfVM -t vbox --label=dbms04 --levo
DIST=MSProducts \ DISTREL=WXP \ OS=MS-Windows \ OSREL=XP \ MAC=00:50:56:13:11:81 \ IP=172.20.10.24 \ ARCH=x86_64 \ MEMSIZE=512 \ ctys-createConfVM --label=dbms04 -t vbox
Not all values require to be set, some will be requested later
by dialogue.
Thus it is not neccessary to have values assigned to the complete
displayed set.
Actually used sources for default values:
no-marker = Pre-Set value, either from defaults configuration,
or by commandline.
no-value = Either requested by dialog later, or the defaults
of the finally called
application are used.
(c) = Read from actual configuration file, e.g. vmx-file.
(d) = Read from database.
(g) = Dynamically generated.
(h) = Used from current host as default.
(m) = Received from mapping definitions.
Applicable modifications:
blue = By call option, defines dependency for others.
green = By environment, 'could be set almost independent'
from other values.
cyan = By miscellaneous facilities, but is dependent from
others.
E.g. LABEL defines by convention the network 'hostname',
thus the TCP/IP params.
This could ..., but should not be altered!
Most of the missing values will be fetched during actual execution of
this tool by dynamic evaluation.
VAR name:Initial Value
C_SESSIONTYPE:VBOX
LABEL:dbms04
MAC:00:50:56:13:11:81 (m)
IP:172.20.10.24 (m)
BRIDGE:
DHCP:
NETMASK:
TCP:dbms04 (m)
GATEWAY:
EDITOR:acue
UUID:
DIST:MSProducts
DISTREL:WXP
OS:Windows
OSREL:XP
ARCH:x86_64 (h)
ACCELERATOR:
SMP:
MEMSIZE:512
KBD_LAYOUT:de
STARTERCALL:/usr/bin/VirtualBox
WRAPPERCALL:dbms04.sh
DEFAULTBOOTMODE:HDD
DEFAULTINSTTARGET:/mntn/vmpool/vmpool01/..
..vbox/mysql/dbms04/dbms.vdi
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_SIZE:
DEFAULTHOSTS:RDP
DEFAULTCONSOLE:RDP
VMSTATE:ACTIVE
Remember that his is a draft pre-display of current defaults.
No consistency-checks for provided values are performed at this stage.
Some missing values are evaluated at a later stage dynamically.
The installation of raw machine is performed here by the native vendor supported tools. These could be started e.g. by using the X11 plugin and execution of a remote command. The advance is the transparent encryption on the inter-node connections by SSH. Ths e.g. in case of problems with the https port the unencrypted http GUI could still be used in a secure manner for network connections. All connections are tunneld by OpenSSH, here the X-displayforwarding with the '-X' option. The start of the VMW console for RHEL-5.5 and VMware Server-2.0.2 is:
ctys -t x11 -a create=l:vmwcon,cmd:vmware root@lab05
This starts the default fornt end, here the Firefox browser.
REMARK: The following figures are copied from another example with identical workflow.
REMARK:
The current version of the UnifiedSessiosnManager requires by convention the coallocation of
the VMX file and the boot HDD.
Particularly the enumeration of VMs requires the presence of the VMX file.
In some cases - for Server-2 when the allocation is altered from the defined storage - these are stored
by default into different directories.
This has to be considered for the allocation of new VMs.
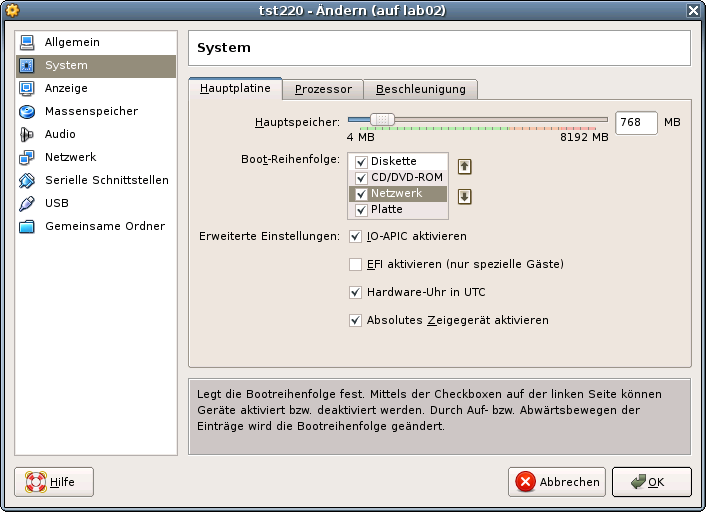
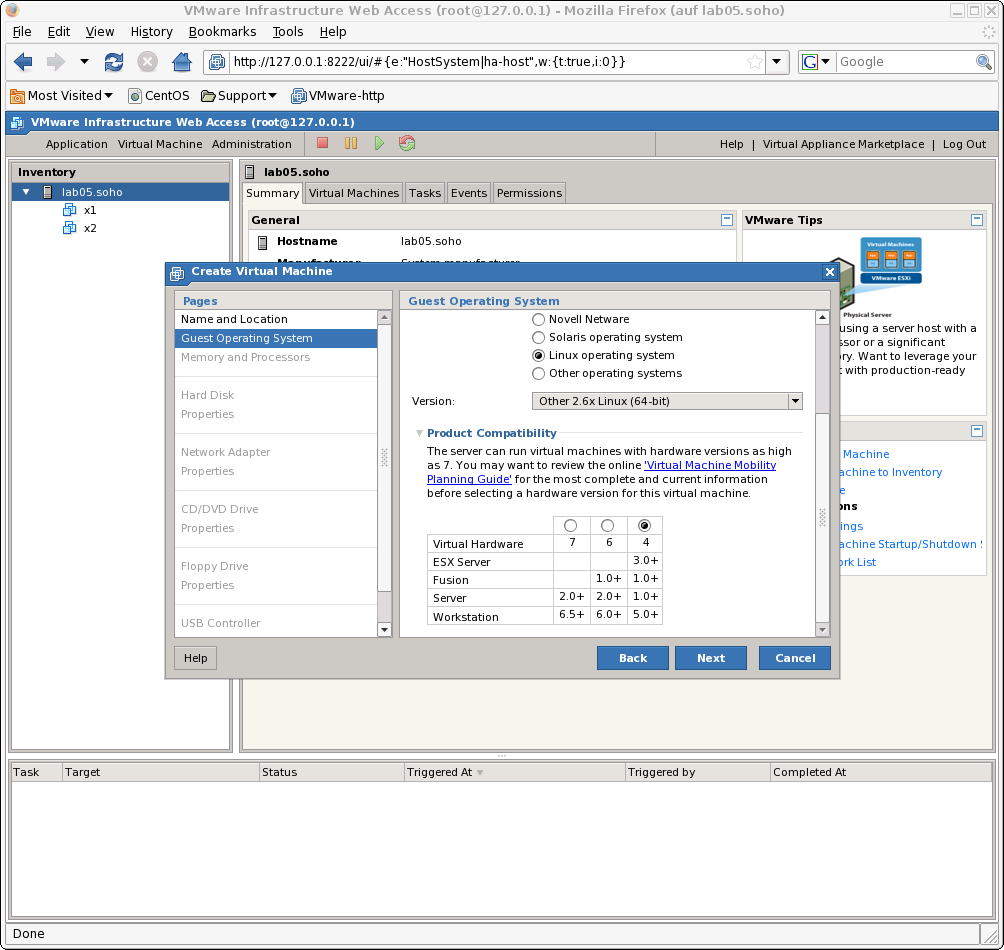
The virtual machine should be selected as hardware version 4 when maximum compatibility is required.
For tight and vendor independent management of the VMs and PMs the MAC addresses should be assigned individually to each machine and centrally managed by DHCP.
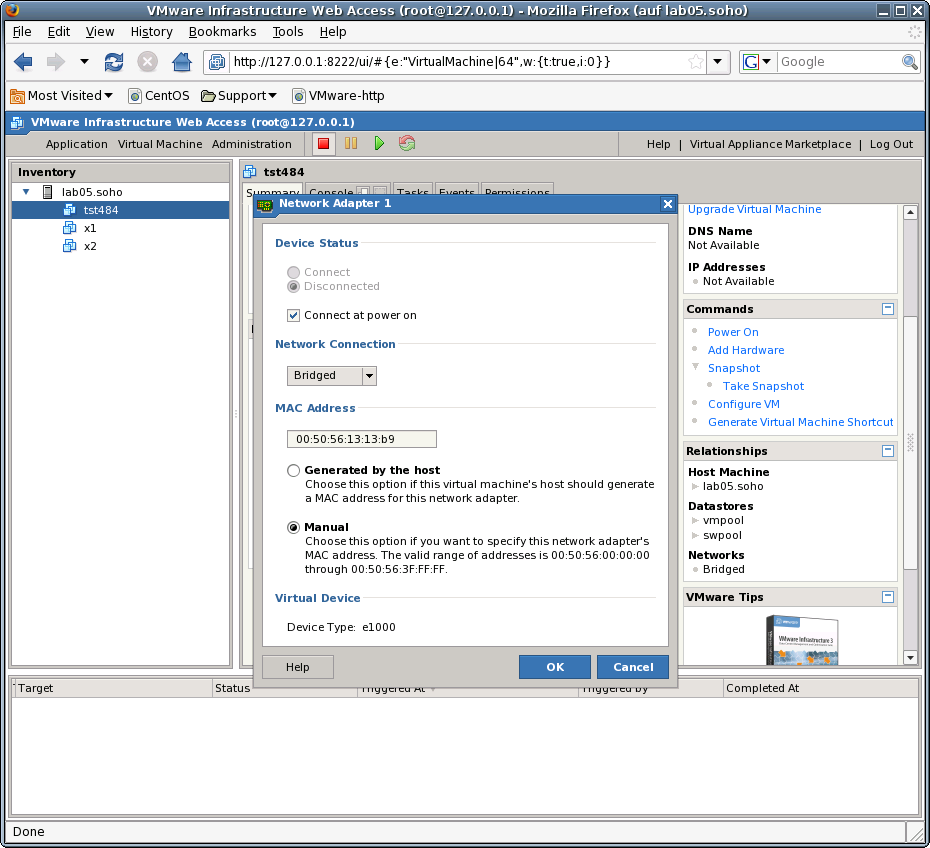
In addition the UUID of the VM should be set to fixed by maunal edition of the VMX file.
This has advantages for unambiguity in networked operating environments.
The UUID is part of the <machine-address> and therefore stored within the database and could be used
for persistent addressing.
Thus should not be changed by a harmless move, due to an algorithm for assurance of generic unambiguity.
Once the setup is finished by means of the vendor tools, the following steps of installation
could be proceeded either continued solely by the vendor provided environment, or by application
of the UnifiedSessionsManager toolset.
The instmode for adaption of the actual boot configuration is not yet supported, thus
a normal startup by management of boot and installmedia by the vendor products has to be applied.
The following operational procedures within the GuestOS are similar for all hypervisors.
Just a few exceptions exist for installing specific driver sets - so called Tools available e.g. for
almost all VMware(TM) products.
These have to be mounted as install media and installed by the provided installer.
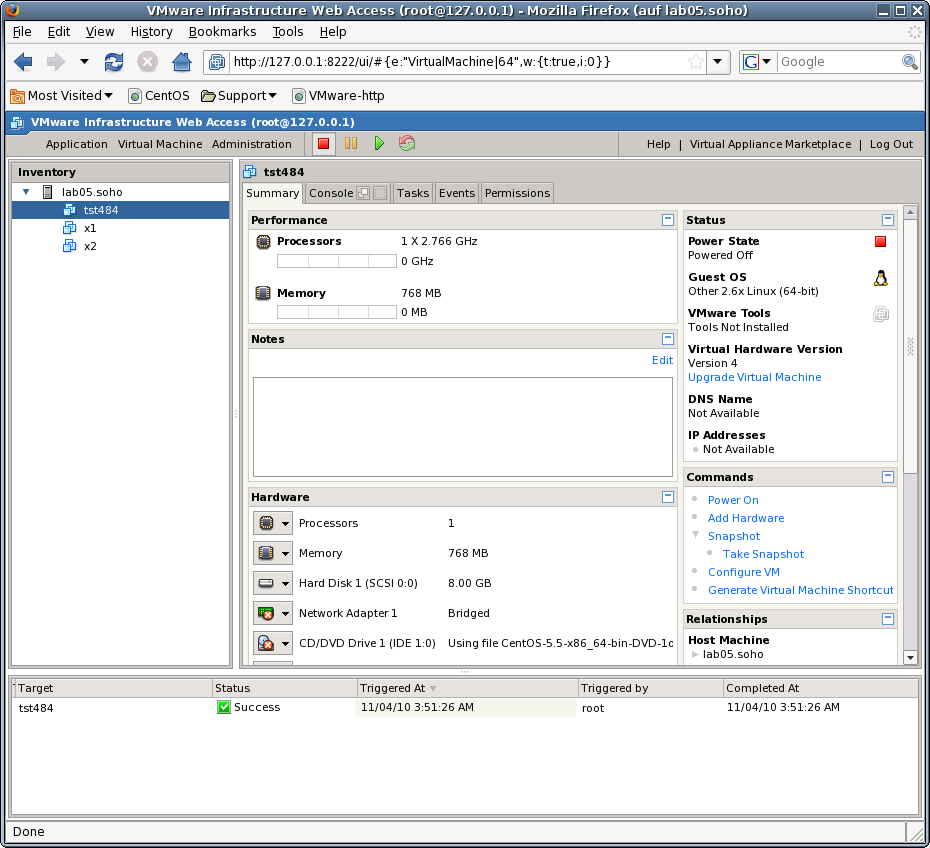
The following demonstrates the reallocation of the machine files to a common directory with the storage devices. The virtual HDD is stored within the directory
[Datastore] vmpool05/vmw/test/tst-ctys/dbms04/dbms04.vmdk
whereas the VM configuration files are stored by the system in the datastore to
[Datastore] dbms04/...
scsi0:0.fileName = "/mntn/vmpo ..." ide1:0.fileName = "/mntn/swpool/UNIXDist..."
uuid.action = "keep"
ethernet0.addressType = "generated" ethernet0.generatedAddress = "00:0c:29:9c:6a:6a"
ethernet0.addressType = "static" ethernet0.address = "00:50:56:13:11:33"
displayName = "dbms04"which is the so called LABEL.
For the management of the GuestOSs and integration into the database of the UnifiedSessionsManager the
inventory functions by ctys-createConfVM and ctys-vdbgen should be at least post-applied once after
finishing the guest installation.
The installed GuestOS is here the same as the HostOS, with the only difference, that the architecture has to be set to 'ARCH=i386'. This reduces the call for configuration creation to:
ARCH=i386 ctys-createConfVM -t vmw --label=dbms04
The --levo display is:
Not all values require to be set, some will be requested later by dialogue.
Thus it is not neccessary to have values assigned to the complete displayed set.
Actually used sources for default values:
no-marker = Pre-Set value, either from defaults configuration,
or by commandline.
no-value = Either requested by dialog later, or the defaults
of the finally called
application are used.
(c) = Read from actual configuration file, e.g. vmx-file.
(d) = Read from database.
(g) = Dynamically generated.
(h) = Used from current host as default.
(m) = Received from mapping definitions.
Applicable modifications:
blue = By call option, defines dependency for others.
green = By environment, 'could be set almost independent'
from other values.
cyan = By miscellaneous facilities, but is dependent from others.
E.g. LABEL defines by convention the network 'hostname',
thus the TCP/IP params.
This could ..., but should not be altered!
Most of the missing values will be fetched during actual execution of
this tool by dynamic evaluation.
VAR name:Initial Value
LABEL:dbms04
MAC:00:50:56:13:13:B9 (c)
IP:172.20.6.184 (m)
BRIDGE:
DHCP:
NETMASK:
TCP:dbms04 (m)
GATEWAY:
EDITOR:acue
UUID:564d99fb5a6c2897edce5b14279c6a6a (c)
DIST:CentOS (h)
DISTREL:5.5 (h)
OS:Linux (h)
OSREL:2.6.18-194.el5 (h)
ARCH:x86_64 (h)
ACCELERATOR:
SMP:
MEMSIZE:768 (c)
KBD_LAYOUT:de
STARTERCALL:/usr/bin/vmware
VMSTATE:ACTIVE
Remember that his is a draft pre-display of current defaults.
No consistency-checks for provided values are performed at this stage.
Some missing values are evaluated at a later stage dynamically.
The result could be inspected e.g. by the following call with one of the standard macros. Called within the directory of the VM, therefore starting at the scan-base 'b:$PWD'.
ctys -t vmw "{MACRO:enumdefault},b:$PWD"
Resulting in the output:
label |stype|accel|distro|distrorel|os |osrel |PM |if|TCP ------+-----+-----+------+---------+-----+----------+----------+--+------------ dbms04|VMW | |CentOS|5.5 |Linux|2.6.18-194|lab05.soho|0 |172.20.6.184
ffs.
ffs.
The examples for installaltion of Xen GuestOSs are performed here on a RedHat-Enterprise-Linux - RHEL-5.5 server.
The procedures are almost identicel to other derived distributions, e.g. CentOS, ScientificLinux, or EnterpriseLinux.
After the boot of the lab-machine start a VNC root console by generated menu entry.
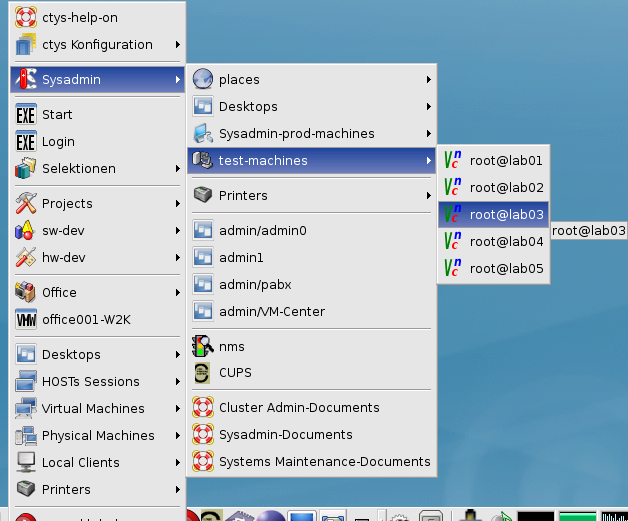
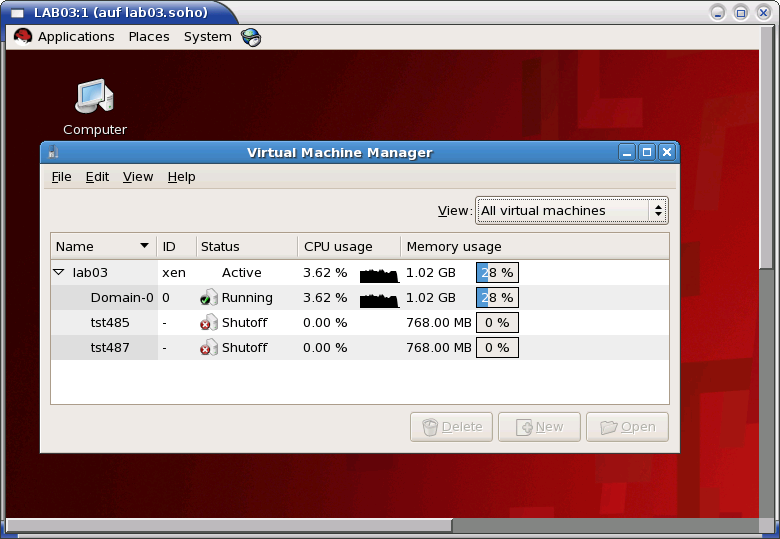
The Xen files, including the Python conf-file and the initial virtual devices are created by the utility
ctys-createConfVM(1)
.
Thus e.g. the MAC address(
ctys-private-MAC-address(7)
)
has to be provided when networking is required.
In some cases - e.g. for OpenSUSE or debian - it might be required to provide the virtual bridge too.
This is due to internal detection a so called Xen-Bridge by searching for the first bridge containing a
'pethX' device, which sometimes varies.
E.g. for debian the bridge is called in some releases simply 'eth0'.
Thus when errors with networking due to missing bridge occurs, than just set an appropriate default.
If this still does not suffice, than the variable 'FORCE_THIS_IS_XEN_BRIDGE=br0' may help(
ctys-configuration-XEN(7)
).
But be aware, when the machine is executed on different machines with various HostOSs, e.g. viy NFS.
Than the bridge names may vary, and may require to be adapted.
This is the reason of dynamic evaluation for the networking devices.
Create a directory where the VM is to be stored. When the automation defaults are setup appropriately in ctys-config-guest-sources(7) the option '--auto-all' creates the complete raw VM by batch-execution. Now execute the call for the complete creation of the VM.
MAC=00:50:56:13:11:81 \
DIST=MSProducts \
DISTREL=WXP \
OS=Windows \
OSREL=XP \
ctys-createConfVM \
-t XEN \
--label=dbms04 \
-C \
-D $PWD/dbms04 \
--auto-all
This creates with the --levo check the output:
Not all values require to be set, some will be requested later by dialogue.
Thus it is not neccessary to have values assigned to the complete displayed set.
Actually used sources for default values:
no-marker = Pre-Set value, either from defaults configuration,
or by commandline.
no-value = Either requested by dialog later, or the defaults
of the finally called
application are used.
(c) = Read from actual configuration file, e.g. vmx-file.
(d) = Read from database.
(g) = Dynamically generated.
(h) = Used from current host as default.
(m) = Received from mapping definitions.
Applicable modifications:
blue = By call option, defines dependency for others.
green = By environment, 'could be set almost independent'
from other values.
cyan = By miscellaneous facilities, but is dependent from others.
E.g. LABEL defines by convention the network 'hostname',
thus the TCP/IP params.
This could ..., but should not be altered!
Most of the missing values will be fetched during actual execution of
this tool by dynamic evaluation.
VAR name:Initial Value
C_SESSIONTYPE:XEN
LABEL:dbms04
MAC:00:50:56:13:11:81
IP:172.20.10.24 (m)
BRIDGE:
DHCP:
NETMASK:
TCP:dbms04 (m)
GATEWAY:
EDITOR:acue
UUID:e589efe5-5fe5-4de8-890c-43484b5a64e4 (h)
DIST:MSProducts
DISTREL:WXP
OS:Windows
OSREL:XP
ARCH:x86_64 (h)
ACCELERATOR:HVM (h)
SMP:1
MEMSIZE:768
KBD_LAYOUT:de
STARTERCALL:/usr/sbin/xm
WRAPPERCALL:/usr/bin/sudo.sh
DEFAULTBOOTMODE:HDD
DEFAULTINSTTARGET:/tmp/b/dbms04/xvda.img
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_SIZE:8G
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_BLOCKSIZE:256M
DDBOOTIMAGE_INST_BLOCKCOUNT:32
HDDBOOTIMAGE_INST_BALLOON:y
DEFAULTINSTMODE:CD
INSTSRCCDROM:/mntn/swpool/cdroms/Microsoft/WXP/wxp-sp2.iso
DEFAULTINSTSOURCE:/mntn/swpool/cdroms/Microsoft/WXP/wxp-sp2.iso
BOOTLOADER:/usr/lib/xen/boot/hvmloader
DEFAULTHOSTS:RDP
DEFAULTCONSOLE:VNC
VMSTATE:ACTIVE
Remember that his is a draft pre-display of current defaults.
No consistency-checks for provided values are performed at this stage.
Some missing values are evaluated at a later stage dynamically.
The following call starts the initial installation of the VM:
ctys -t xen -a create=l:dbms04,reuse,b:$PWD,instmode root@lab03
ffs.

ctys -t qemu -a cancel=l:dbms04,b:${VMDIRECTORYPATH},poweroff app2
The syntax for this is similar for all supported hypervisors.
The following call starts the VM into standard operations.
ctys -t qemu -a create=l:dbms04,b:${VMDIRECTORYPATH} app2
Once the basic post-install configuration is finished the machine reboots into the normal operations mode.

In case of a common mounted NFS filesystem for the pool VMs for simplicity just change into the directory of the VM on any machine. Call for the first check ctys-vdbgen with the --stdio option for display only.
ctys-vdbgen --append --base=$PWD --stdio -- lab02
When the result is displyed correctly just call
ctys-vdbgen --append --base=$PWD -- lab02
The following output should be displayed:
Prepare execution-call:
Require DB-PATH, USE: DEFAULT_DBPATHLST="/homen/acue/.ctys/db/default"
Require DB-PATH, USE: -o => "/homen/acue/.ctys/db/default"
APPEND mode : ON(1)
STDIO mode off : OFF(0)
Set TYPE scope ADD: DEFAULT="-t ALL"
Preload TYPE set ADD: DEFAULT="-T ALL"
For splitted operations ADD: DEFAULT="-b sync,seq "
Nameservice cache OFF: DEFAULT="-c off "
Data cache OFF: DEFAULT="-C off "
Resulting ENUMERATE ADD: DEFAULT="-a enumerate=...
...matchvstat:active%disabled%empty,machine,\
b:/mntn/vmpool/vmpool05/vbox/test/tst-ctys/dbms04 \
-C off -c off -T ALL "
-> generate DB(may take a while)...
-----------------------------------
START:08:38:35
------
------
END:08:39:03
DURATION:00:00:28
-----------------------------------
RET=0
-----------------------------------
Cached data:
Mode: APPEND
Pre-Appended: 834 records
Appended: 1 records
Fetched Records Raw: records
Fetched Records Unique: records
Final: 835 records
-----------------------------------
...finished.
This shows that only one entry is appended to the existing database with 834 VM-Entries. Now check the database entry by calling:
ctys-vhost dbms04
The following result should be displayed:
label |stype|accel|distro|distrorel|os |osrel|PM |if |TCP ------+-----+-----+------+---------+-----+-----+-----+---+------------ dbms04|VBOX | |CentOS|1.0.0 |Linux|2.6 |lab02|0 |172.20.2.241
Now call the menue item for start of the VM 'dbms04'.
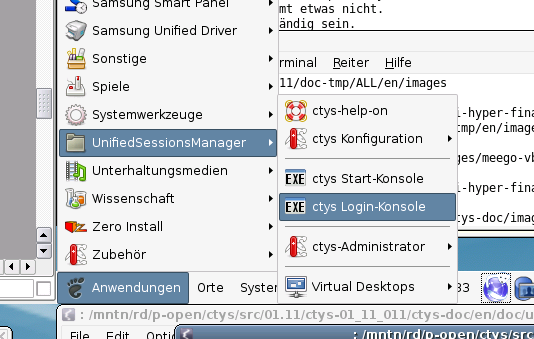
The created cacheDB record for thr VM 'dbms04' is now automatically visible in the
list of startable virtual machines.
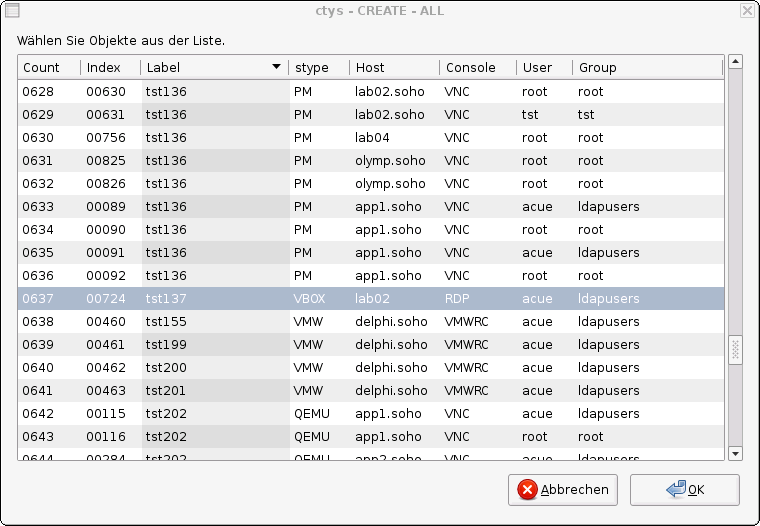
Confirm the selected entry.
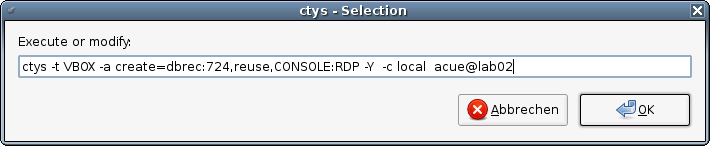
Install and configure the MS-Windows-XP(TM) guest system as required.
The following call starts the VM
cd /mntn/vmpool/vmpool01/kvm/mysql/dbms04 ctys -t qemu -a create=l:dbms04,b:$PWD,reuse app2
The opened console is here by default VNC for the QEMU/KVM hypervisor.
For the use of a RDP based console with MS-Windows-XP(TM) the following call starts an RDP session.
ctys \
-t rdp \
-a create=l:dbms04,rdphost:dbms04,user:administrator%xy%dbms04,reuse \
-L cF \
-g 500x300 \
app2
This starts a session in CONNECTIONFORWARDING mode, which implicitly creates
an SSH-tunnel for a local rdesktop client.
This call performs a completet login and sizes the window by 500x300 pixels.
The size for the terminal server window could be changed for each call independently
from the size of the configured server resolution.
Download the intstaller 'setup.exe' and if required mirror the packages from www.cygwin.com . Install the default packages, this must be executed as local Administrator, else you may encounter various problems by security assertions of various tools due to wrong ownerships of files and directories. This is particularly the case true when the installation is proceeded as domain admin and and the SSH service does not start. In case of errors check for SSH first the call from command line
/usr/sbin/sshd.exe
The following packages are installed in addition to the default set.
The configuration of an ssh server for windows is setup here based on Cygwin and OpenSSH. For the original source of the following receipt refer to
http://hydra.geht.net/tino/howto/cygwin/cyg--ssh
by Mr. Valentin Hilbig.
First install and configure SSH access, therefore call the shell by cygwin.bat and proceed as follows. The procedure has to be executed as Administrator.
mkpasswd -l > /etc/passwd mkgroup -l > /etc/group /usr/bin/cyglsa-config
and reboot the machine or shutdown and start by
ctys -t qemu -a create=l:dbms04,b:$PWD,reuse app2'(-d 1,pf)'
Attach an RDP desktop
ctys \
-t rdp \
-a create=l:dbms04,rdphost:dbms04,user:Administrator%-%dbms04,reuse \
-L cF \
-g 1000x900 \
app2
Now call
ssh-host-config -y
Activate the X11-Forwarding in /etc/sshd_conf by
X11Forwarding yes
The next calls prepare and start the server as a service.
cygrunsrv -S sshd
When errors occur restart the procedure by initial reboot of the SSH daemon
cygrunsrv -R sshd
Now copy e.g. your key from a remote client
ssh-copy-id Administrator@dbms04
Call CLI plugin:
ctys -t cli -a create=l:dbms04 root@dbms04
Call ctys-plugins:
ctys-plugins -T all -E
ffs.
Call VNC plugin:
ctys -t vnc -a create=l:dbms04,reuse root@dbms04
Call VNC plugin:
ctys -t x11 -a create=l:dbms04,reuse root@dbms04
ctys-configuration-QEMU(7) , ctys-configuration-VBOX(7) , ctys-createConfVM(1) , ctys-plugins(1) , ctys-QEMU(1) , ctys-uc-QEMU(7) , ctys-uc-VBOX(7) , ctys-vhost(1) , ctys-uc-VMW(7) , ctys-VBOX(1) , ctys-VMW(1) , vmware(1)
For System Tools:
CentOS: [ http://www.centos.org ]
RedHat(TM): [ http://www.redhat.com ]
| Arno-Can Uestuensoez | <https://arnocan.wordpress.com/> |
| <https://unifiedsessionsmanager.sourceforge.io/> | |
| <https://github.com/unifiedsessionsmanager> | |
 |
Copyright (C) 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2020 Ingenieurbuero Arno-Can Uestuensoez
For BASE package following licenses apply,
This document is part of the DOC package,

For additional information refer to enclosed Releasenotes and License files.